November 21, 2023 17 min read

Keep EMS Providers Engaged, Informed, and Compliant with New and Updated CAPCE-Accredited Continuing Education
Industry:
Solution:

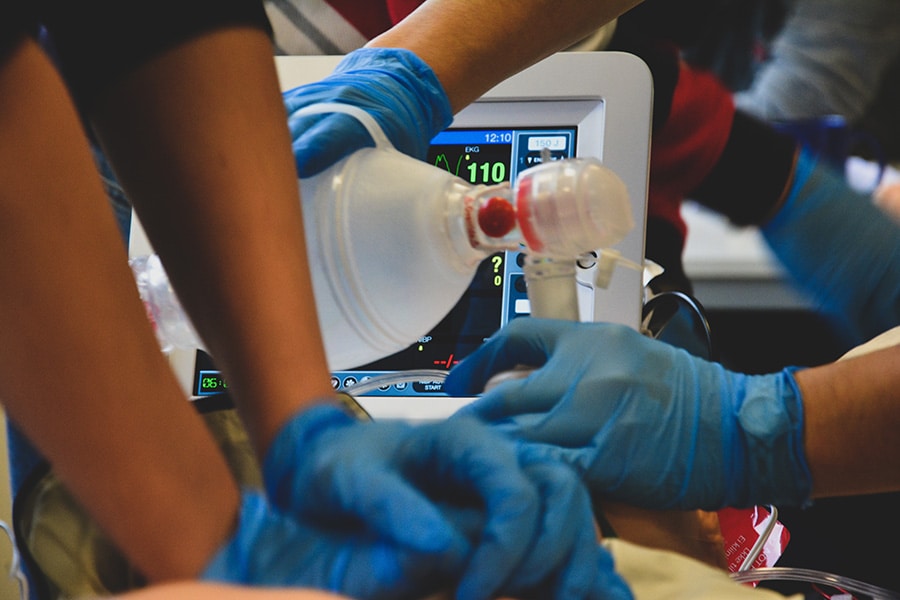
In the dynamic landscape of emergency medical services (EMS), where split-second decisions can make the difference between life and death, the importance of providing EMTs and paramedics with access to vetted and up-to-date training cannot be overstated.
Vector Solutions, organizationally accredited by the Commission on Accreditation for Prehospital Continuing Education (CAPCE), offers more than 250 hours of online EMS continuing education to help EMS providers at every level meet recertification requirements, stay safe, and boost readiness.
Know that you’re providing your EMS personnel with the most up-to-date, evidence-based data and protocols, including recent statistics, case studies, and research. Our EMS catalog is continuously refreshed with new and updated courses to help providers keep up with the ever-evolving environment of emergency medical services and meet NREMT continuing education requirements.
The Vector LMS training management platform makes it easy to assign, track, and monitor EMS training with organized pre-built EMS training trackers structured by NREMT hour and category requirements by EMS level.
Learn More >
Reduce the burden on administrators and providers to find and review EMS continuing education content, simplify certification tracking, reduce overtime with online training, mitigate liability risks, and strengthen compliance with a purpose-built learning and training management system for EMS.
From courses pertinent to effective patient response to emerging threats like gunshot wounds and bomb blast injuries, treating invisible threats like carbon monoxide poisoning, and addressing core topics like cardiac arrest and pediatric trauma, our interactive online courses keep providers engaged and informed.
Check out the full list of updated and new courses released in our EMS continuing education catalog in 2023:
- Altitude Emergencies
1 hour
The Altitude Emergencies course provides comprehensive knowledge and skills for managing altitude-related medical emergencies. Ascent into high altitude puts the body in danger in several ways. With altitude illness, hypothermia, and frostbite being significant risks at high altitudes, this course covers the pathophysiology, signs, symptoms, and appropriate care for each condition. Participants will gain a deep understanding of the prevention and treatment of altitude illness, as well as the assessment and management of patients with hypothermia and frostbite.
By the end of the course, participants will be equipped to recognize and provide prompt and effective care for altitude-related emergencies, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients in these challenging environments.
- Assessing the Patient with Major Trauma
2 hours
This course discusses assessment techniques for making the initial impression of patients as well as assessment elements specific to certain types of trauma injuries. A quick and thorough assessment of a trauma patient is the cornerstone for providing proper treatment and may aid in preventing death or permanent disability.
- Assessment and Treatment of Sexual Assault Patients
1 hour
This course focuses on preparing EMS workers to effectively respond to incidents of drug-facilitated sexual assault, which can pose numerous challenges for responders. The course covers the incidence, effects, and characteristics of these types of emergencies, as well as patient management procedures and treatment interventions.
Through this course, EMS workers will gain cultural competence for victims of sexual assault and learn how to approach these types of calls with empathy and respect.
- Asthma Advanced
1 hour
In this course, you will be presented with a variety of interesting opportunities to increase your understanding of how adults and pediatrics are continuously being impacted by asthma disorders and emergencies each day. You will have the chance to deepen your knowledge about the anatomy and pathophysiology that causes and affects asthma disorders in adults and pediatrics.
Relevant medical case studies, medical terminology, and assessment strategies are presented, along with researched medications for treatments for use by BLS and ALS for patients with mild and severe asthma emergencies. The course will help you increase your confidence and base knowledge of awareness and skills you can apply in the field to provide the best patient care for adult and pediatric patients who are experiencing asthma emergencies.
- Basics of Arrhythmias: Tachy-arrhythmias and Fibrillation
1 hour
More than 250,000 people each year are treated by EMS professionals for cardiac arrest. The most common causes of these types of cardiac arrests are ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. This course covers the causes and treatments for tachyarrhythmias and fibrillation.
- The Basics of of Cardiac Arrhythmias and Premature Complex Rhythms
1 hour
In this course, students will learn different aspects of arrhythmias that can cause people to experience premature cardiac rhythms in prehospital settings. This course will cover the primary anatomy and physiological structures of the heart. Students will learn how premature rhythms affect patients in the prehospital setting and how to identify irregular rhythms on EKGs. It also reviews terminology associated with the heart and irregular rhythms and treatment and therapies used by EMS and Health care workers in prehospital settings for patients experiencing premature and irregular arrhythmias.
- Behavioral Emergencies
1 hour
Emergency services personnel respond to many situations involving behavioral emergencies. Some of these emergencies will be the result of an injury or acute illness of the patient. Others will be the result of a mental illness or the use of mind-altering substances. Mental health issues incapacitate more people than all other health problems combined.
The National Institute of Mental Health estimates that one in five American adults will suffer from a mental illness every year. Research into the underlying origins of many EMS calls correlate underlying mental illness as the cause for up to eighty percent of the requests for care from the most frequent callers.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
1 hour
This course is designed to provide EMS responders with a comprehensive understanding of carbon monoxide poisoning. Carbon monoxide is a common toxin that is often misdiagnosed, making it important for EMTs and paramedics to have a thorough understanding of its effects and best practices for treating patients. Through case-related examples, the course covers the effects of exposure, symptoms, treatment procedures, and personal protective equipment best practices.
By the end of the course, learners will be able to explain how carbon monoxide poisons its victims, identify symptoms, and perform proper treatment procedures.
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology Review
1 hour
For over 80 years, cardiovascular disease has been the leading cause of death in the U.S. More than 80 million people in America suffer from some cardiovascular disease. Of these, coronary heart disease is the most prevalent. It remains the leading cause of death nationwide. Because of the prevalence of cardiovascular conditions, it is essential for EMS personnel to understand the anatomy and physiology of the heart and the vascular system.
- Capnography
1 hour
This course covers the use of capnography in prehospital patient care. Capnography measures the levels of carbon dioxide in exhaled air. It can be used to assess proper tube placement following intubation, but has many other uses as well. When combined with other diagnostic tools, it can provide a complete picture of what may be happening to the patient. This course covers the use of both colorimetric devices and digital monitoring, including capnometry and capnography. Objectives include recognizing the relevance of end-tidal CO2 as a prognostic tool, applying capnography concepts to patient differential diagnoses, interpreting end-tidal CO2 levels, and summarizing the basics of carbon dioxide and its role in the body.
- Clinical Decision-Making
1 hour
This course is designed to help EMS providers develop strong clinical decision-making skills in the pre-hospital environment. Providers must be able to gather and synthesize information quickly and develop patient management plans in changing conditions.
The course covers factors that influence medical care in the pre-hospital environment, benefits and shortfalls of different scopes of practice, differentiation of patient conditions, critical thinking processes, and mental health factors that may impact an EMS worker’s ability to think critically on scenes. Upon completion, providers should be able to apply critical thinking elements and make effective decisions in the pre-hospital environment.
- Common Infectious Pathogens
1 hour
This course covers the fundamentals of infectious diseases and their prevention, including the definitions of key terms such as pathogen, port of entry, and PPE. Learners will also gain a basic understanding of common diseases like Hepatitis, Tuberculosis, and MRSA, and how to safely decontaminate people and equipment. By the end of the course, learners will have a solid foundation of knowledge to help prevent the spread of infectious diseases in various settings.
- Communication and Documentation
1 hour
Communication is at the center of what and how we, as emergency responders fulfill our professional responsibilities. How we listen and interact with 9-1-1 calling parties, dispatchers, co-responding agencies, allied health professionals, and others will determine whether those interactions are positive and successful or negative opportunities. Communication isn’t related solely to the verbal realm. There is also non-verbal and written communication that will also be a part of every response that we go to.
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
1 hour
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is a collection of diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are used by millions of Americans to treat or lessen disease. This course explores common CAM treatments, their impact on EMS, and the adverse effects of some CAM treatments and supplements.
- Emergency Response to Terrorism (4 modules)
4 hours
The Emergency Response to Terrorism course series is a four-module program designed for first responders to provide them with an understanding of “awareness level” concepts for responding to potential terrorist incidents. The course covers topics such as terrorism overview, recognizing suspicious incidents and warning signs, self-protection, and scene control and coordination. The course emphasizes the importance of staying alert, taking breaks, and reviewing notes to retain the large quantity of information provided.
After completing the course, first responders will be able to recognize attack vulnerability factors, identify potential terrorist threats, and distinguish the chief characteristics of terrorist activities.
- Environmental Emergencies
1 hour
Environmental emergencies include exposure to both heat and cold. Regulation of body temperature, which is an important physiological function, can be impaired under temperature extremes and result in heat or cold-related illness. The key to effective management is recognizing the signs and symptoms and providing prompt emergency medical care.
- Epilepsy
1 hour
This course covers the recognition, assessment, and management of patients with seizures, with a focus on the challenges faced by EMS personnel. It covers the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and different types of seizures, as well as the approach to patient assessment and management priorities. Additionally, the course discusses the importance of discerning a patient’s medical history and medications when responding to seizure incidents.
- Grey Area Calls
1 hour
This course explores the “grey areas” of EMS medical calls where patient complaints and symptoms may be less clear than textbook examples. The course focuses on developing a thorough assessment process, utilizing advanced instrumentation tools and point of care testing to identify potential prodromes and form clinical impressions, and selecting the correct emergency treatments and interventions for patients. The course also covers grey area concepts in medical, trauma, and psychiatric patient subsets, as well as medical-legal considerations. By the end of the course, learners will have enhanced assessment confidence and capability in making grey area decisions of consequence.
- Gunshot Wounds and Bomb Blast Injuries
2 hours
EMS providers at all levels are often faced with the challenge of responding to scenes of targeted violence and treating patients with gunshot wounds or blast injuries. Penetrating trauma caused by firearms presents a unique challenge for EMS personnel due to potential severity of gunshot injuries to the human body, complex implications in patient care, and the unpredictability of the scene during and after a violent incident has taken place. These dynamic and often volatile scenes create new and unique challenges for the responder.
This course will help prepare you for this response, by providing insight into the unique attributes of a bomb blast situation, and the injuries you might encounter.
- Hazard Communication
1 hour
Exposure to hazardous chemicals can present numerous dangers to workers. More than 30 million workers are exposed to one or more chemical hazards across various industrial sectors. And with hundreds of new hazardous chemicals being introduced annually in addition to the estimated 650,000 already existing hazardous chemical products, the risk is increasing every year. This poses a serious problem for many workers and their employers.
OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS), sometimes referred to as the Right-to-Know regulation, is designed to ensure that information about these dangers is shared with those who need to know. Chemical manufacturers, distributors, and importers must convey hazard information to downstream employers by means of labels on containers and safety data sheets (SDSs). In addition, all covered employers must have a hazard communication program to get this information to their employees through labels on containers, SDSs, and training.
This course covers the HCS with an emphasis on what it is and how to comply, and incorporates recent changes made to the standard in accordance with the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. HCS provides guidelines to help prevent chemical hazard incidents and the adverse health effects that may result.
- Hazmat Medical Emergencies
1 hour
In the HazMat Medical Emergencies course, ALS personnel will explore advanced concepts and care related to hazardous materials (HazMat) incidents. This course serves as both an introduction and a refresher for ALS-trained individuals working in the HazMat specialty. Prior knowledge of Advanced Life Support (ALS) medical terminology and a basic understanding of chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, and high yield explosives (CBRNE) concepts are prerequisites for this course.
By the end, participants will have the ability to discuss advanced concepts of care, recall essential terminology and historical data, identify toxidromes, describe the physiological effects of toxic agents, and discuss pharmacology in HazMat medical emergencies.
- Heat Illness and Emergencies
1 hour
This course provides an in-depth understanding of temperature regulation in the human body and the impact of extreme temperatures on our health. Students will learn about the signs and symptoms of heat illnesses, such as heat stroke, heat cramps, and heat exhaustion, as well as assessment, treatment, and management procedures for these conditions. Special considerations for elderly and pediatric patients will also be covered.
By the end of the course, students will be able to recognize, prevent, and manage heat-related illnesses.
- Hematology
1 hour
This Hematology course covers the study of blood and the various organs that form blood, including the function of different elements of blood and blood typing. Hematological disorders such as anemia, hemophilia, lymphoma, and sickle cell disease are discussed, as well as how prescription medications can alter blood composition and worsen underlying disease. The course aims to broaden the skills of first responders in assessing and treating hematologic emergencies, including critical thinking about hematology and integration of new concepts into patient care scenarios.
After completing the course, learners will be able to define hematology, identify hematologic disorders, and recall various hematology terms and definitions.
- Incident Command System (ICS): with Applications for EMS
1 hour
In the aftermath of the 9/11 attacks on the World Trade Center, Pentagon, and in Pennsylvania, the Incident Command System (ICS) was implemented across the United States to enable multiple responding agencies to better function as a unified force within the complicated and demanding environments of large-scale and mass-casualty incidents. This course provides an overview of the incident command system with an emphasis on EMS operations.
- Kinetics of Trauma
1 hour
This course focuses on increasing knowledge and awareness of trauma care for Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Life Support (ALS) personnel in prehospital and location-based settings. The course covers various aspects of trauma care, including the management and treatment of trauma patients, prevention of trauma-related deaths, and understanding the physics and mechanisms of traumatic injury. Students will learn about predicting injury based on motion and forces involved in accidents, different types of traumatic injuries, injury patterns associated with specific mechanisms, and recognizing signs of injury in different body systems.
Successful completion of the course will enable students to summarize injury prevention examples, formulate an index of suspicion based on assessment findings, and analyze injury patterns based on trauma mechanisms.
- Managing Cardiac Arrest: During and After Resuscitation
2 hours
Managing Cardiac Arrest: During and After Resuscitation focuses on preparing professional rescuers for emergency situations involving cardiac arrest.
This course covers the causes and progression of cardiac arrest, the components of high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and the principles of assessment for cardiac arrest patients. It also teaches responders how to formulate a rapid intervention plan for an adult patient in non-traumatic cardiac arrest and describes commonly used pharmacological agents for managing cardiac arrest.
- Managing Chronic Care Patients
1 hour
This course is designed to provide EMTs and paramedics with an overview of managing chronic care patients. It covers topics such as the types of medical devices encountered, common complications in chronic care patients, and unique assessment and management strategies. The course aims to help participants develop an understanding of pathologies and complications in home care patients, recognize different complications related to airway, vascular access, and GI/GU devices, and demonstrate appropriate interventions in various chronic care scenarios.
Successful completion of the course will equip participants with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively care for chronic care patients in emergency situations.
- Managing Multiple Casualty Incidents
1 hour
EMS providers respond to varying emergencies, along with fire department and law enforcement personnel, on a regular basis. From time to time, large-scale events occur that require a greater number of first responders and specialty personnel to assist at the incident which will tax local resources and require mutual aid. These events may be a multiple alarm fire or an uncontrolled wildland fire. They may result from transportation accidents involving passenger vehicles, vehicles carrying freight, or both. They may involve a hazardous materials incident or random acts of violence, such as an active shooter. They ultimately can be any situation that involves the challenges that come with managing multiple patients.
- Mechanics of Breathing
1 hour
This course focuses on the Mechanics of Breathing and is aimed at increasing knowledge and awareness of concepts and care for Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Life Support (ALS) personnel. The course covers the structures and functions of the upper and lower airways, the physiological processes involved in respiration, the regulation of respiration, and normal respiratory rates, volumes, and lung capacities for adults, children, and infants. The course also covers the care and treatment of patients with various conditions and situations related to the mechanics of breathing, within the level of training and scope of care of EMTs and paramedics, as well as medical protocols and standard operating procedures.
- Medication Errors
1 hour
This course addresses the critical topic of medication errors in the prehospital setting. It explores the reasons behind medication errors, the potential consequences they can have for patients and providers, and the legal and ethical responsibilities of EMS personnel in medication administration. The course emphasizes the importance of error reporting and provides strategies for preventing medication errors.
By the end of the course, students will be able to analyze the incidence and consequences of medication errors, summarize appropriate documentation practices, and implement prevention strategies to improve patient safety.
- Medical Extrication and Rescue
1 hour
Rescue and extrication operations, especially those relating to traffic incidents, represent a large number of EMS calls. These calls are often not only time-consuming but can be extremely technical, stressful and time-sensitive. Rescuers must have the skills to remain calm while determining the best method of rescuing the patient and subsequently executing their plan.
This course will discuss the phases of a rescue operation, the hazards involved with the types of rescue operations, and the strategies for a successful operation.