AC Motor Operation and Types
DC, or direct current is the electricity that flows in a single direction within a circuit or motor. AC, or alternating current, is the electricity that flows back and forth. The main components of an AC induction motor are the rotor and the stator. The motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy when the rotor is pulled by the fluctuating magnetic field in the stator. This course will discuss single-phase and three-phase motor construction and operation.








Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe alternating and direct current (AC and DC) • Describe single and three-phase power • Describe single-phase motor construction and operation • List and define the different types of single-phase motors • Describe three-phase motor construction and operation • Describe the differences between single-phase and three-phase motors
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an AC motor used for?
What is the difference between AC electricity and DC electricity?
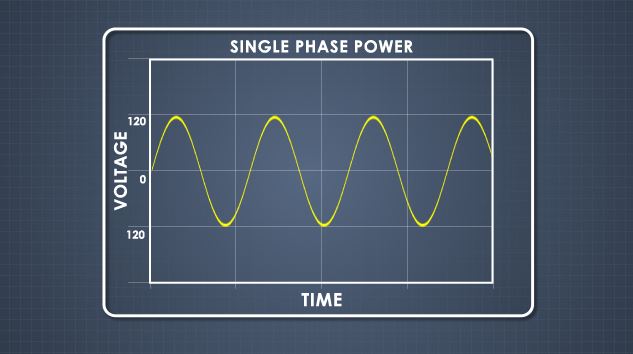
What is single-phase power, and what does it do?
What are the three types of single-phase AC motors?
Why are three-phase motors different from single-phase motors?
Sample Video Transcript
Electric motors are key components of many consumer products and industrial processes, from kitchen mixers to pump motors generating thousands of horsepower. Motors that use alternating current, or AC, are the most common type of industrial electric motor, because they are very low maintenance and extremely reliable. Low-power applications can be satisfied with single-phase motors, whereas higher-power applications or applications where the size or weight of the motor is important may require a three-phase motor. Before describing how an AC motor works, we must first understand the difference between direct and alternating current, and between single and three-phase power.