Fastener Basics
Devices that are used to connect two or more objects together mechanically, are called “fasteners.” There are countless types of mechanical fasteners, and each one is specifically designed for a particular application. This module will identify and describe screw types, identify and describe bolt types, and describe how to use a torque wrench.








Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Define screw, bolt, nut, washer, and torque wrench • Identify and describe screw types • Identify and describe bolt types • Describe fastener diameter, length, and thread count • Describe how to use a torque wrench • Describe why torque wrench extensions are used
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a fastener?
What are some common types of screws?
How are bolts different from screws?
How are screws and bolts measured?
What is torque?
Sample Video Transcript
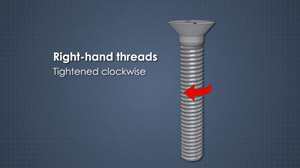
Even though the term “screw” and “bolt” are often used interchangibly, they are different. A bolt is a threaded fastener, like a screw, but it is held in place either by a nut or a threaded hole on the other side. The most common types of bolts include: hex bolts, which are primarily used in machinery and construction, lag bolts, which are large wood screws with hex heads and used in wood construction and landscaping, carriage bolts, which have smooth rounded heads with a square section to pull deeply into the material to stop any spinning during installation, eye bolts, which have a circular loop on one end, so that rope or chain can be attached to it, u-bolts, which are formed in a u shape and used to affix piping or other objects with round surfaces to a material, and studs, which are bolts without heads and threaded on both ends.