July 7, 2017 17 min read
Paper Manufacturing Safety Tips: Hazards, Controls, and Safe Work Practices
Industry:
Solution:

If you’re a paper manufacturer, we probably don’t need to tell you that (1) paper manufacturing comes with its own unique set of hazards, (2) controlling those hazards and keeping employees safe on the job is important and worthwhile, and (3) not only is creating a safe workplace the right thing to do, it pays off in terms of better operational efficiency and higher revenues too. So you may be looking for some paper manufacturing safety tips.
We partner with many paper manufacturers to make online paper manufacturing training videos, both custom and off-the-shelf. And all our customers see the value in online paper manufacturing safety training courses as well.
In the article below, we give a few tips about safety issues when working around a paper machine. The images are taken from our Paper Machine General Safety online course. We’ve included a sample video of that course immediately below, and throughout the article, you’ll see other sample videos from other related courses.

Vector EHS Management Software empowers organizations – from global leaders to local businesses – to improve workplace safety and comply with environmental, health, and safety regulations.
Learn more about how our software can save you valuable time and effort in recording, tracking, and analyzing your EHS activities.
Learn more about how we can help:
- Incident Management Software →
- EHS Inspection Software →
- Key Safety Metrics Dashboard →
- Learning Management System (LMS) and Online Training Courses →
- Mobile Risk Communication Platform
Download our EHS Management Software Buyer’s Guide.
Paper Manufacturing Safety Tips
There are many types of dangers associated with paper making and converting facilities. These dangers can cause severe injury to you or your co-workers.
We’ll start this article by looking at some common hazards found around paper machines, and give you some simple ideas of how to stay safer in their presence.
Then we’ll look at some more general safety precautions to use at a paper manufacturing facility.
In general, keep the following in mind to keep your work environment safe:
- Follow approved procedures at all times
- Receive proper training on equipment and tasks
- Pay attention to your own personal safety and the safety of others
- Maintain a clean, organized facility
Paper Machine Hazards
There are a number of hazards commonly found around paper machines. Being aware of the types of hazards will help you identify, control, and/or avoid harm from specific instances of each.
We’ll list some of the most common.
Pinch Points
Pinch points are places where a person or a body part can be caught or crushed by equipment movement.
Pinch point hazards can be found:
- Between moving machine parts
- Between a moving part and a stationary part
- Around or beneath loads being transported or hoisted
- Between mobile equipment and other machinery or objects
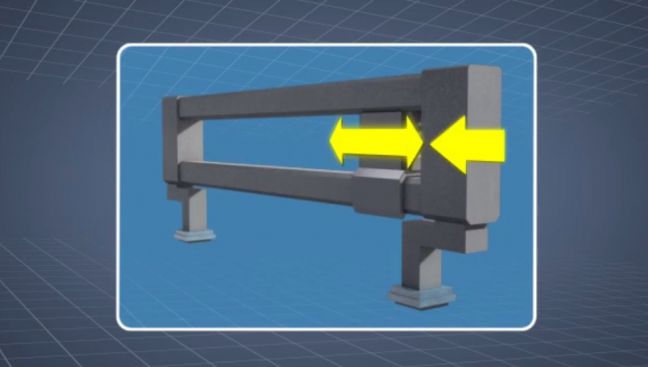
It is common practice to install single point or barrier guarding, or other engineering measures to prevent pinch point injuries. Identifying, proper reporting, and resolution of potential dangers should be an ongoing effort for all employees.
Nips
Nips are a type of pinch point usually associated with adjacent rotating rolls, a rotating roll and a moving rope or web (like a fabric or sheet of paper), or moving ropes and rope sheaves. Nips are hazardous to fingers and hands because they are often present where materials must be fed into the process or at adjustment and lubrication points.
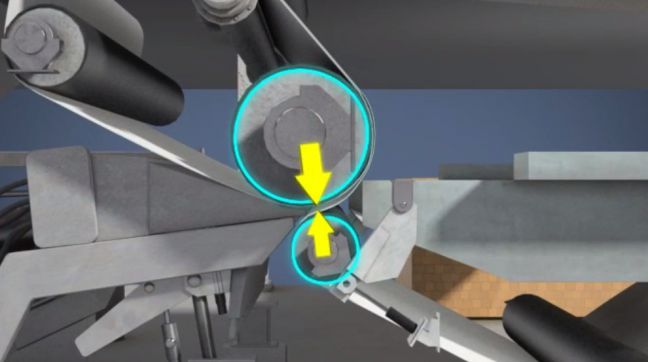
Ingoing nips are located where two machine parts first meet and one or both parts rotate. Ingoing nips can pull fingers, hands, hair, jewelry, and even entire bodies into equipment and machinery. This can lead to serious injuries, including abrasion, amputation, and even death.
An outgoing nip is opposite of the ingoing nip and also presents a hazard. If an object were to enter an ingoing nip, it would be accelerated to the speed of the paper machine and become a dangerous projectile when it exits.
Sharp Surfaces
Sharp surfaces are objects or machine parts that can scratch, puncture, or lacerate the skin.

Be cautious of sharp surfaces when:
- Working with your hands. Hand injuries are the most common injuries associated with sharp surfaces.
- Using tools that are sharp by design, like saws and knives. For example, when using a utility knife, always cut away from your body.
- Working around moving fabrics on paper machines. Bumping up against the edge of a moving fabric will cause a very serious cut.
- Handling doctor blades and worn creping blades. Always follow established procedures and wear all required PPE for your location.
- Performing new or unfamiliar tasks. Be alert for metal burrs, protruding bolts, and sharp or rough edges.
Hot Surfaces
Hot surfaces are another common hazard in a paper manufacturing facility.
Machine surfaces can be hot because they are designed to produce or transfer heat, or because the friction created by machine movement has caused them to become hot. Some potential hot surfaces on a paper machine include steam lines, steam traps, pumps, and the motor on a forklift.

Be aware that hot surfaces may sometimes remain hot for minutes, or even hours, after a machine has been turned off. If you are unfamiliar with a machine, don’t touch its surface unless you are sure it is safe.
Slips, Trips, and Falls
Slips, trips, and falls are responsible for many industrial facility injuries, and they’re a serious concern at paper manufacturing facilities as well. Injuries ranging from cuts and bruises to broken bones, paralysis, and even death can result from falls at ground-level or from only a few feet.

Some leading causes of fall injuries in papermaking facilities include:
- Objects left on the floor, such as broke paper and scraps
- Slippery fluids left on the floor, like water at the wet end of a paper machine where a lot of water and steam are used
- Insufficient or missing railings
- Poorly designed steps
- Not using ladders correctly
- Not using proper fall protection
- Not paying attention to surroundings
For more information, you may want to check out our Slips, Trips, and Falls online course and/or our Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention Inspection course.
Slips, Trips, and Falls Online Course
Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention Inspection Online Course
Airborne Particles
The papermaking and converting processes produce paper fiber dust that accumulates on the machinery and ground.
Dust can be a hazard for several reasons:
- It can be slippery when collected on a walkway
- It can easily get into an operator’s eyes
- When airborne, it can create a risk of fire or explosion
- When airborne, it can cause respiratory problems

Some processes are equipped with enclosures and dust removal systems to minimize dust accumulation. However, it is still important that housekeeping practices are followed. Maintenance and operations personnel should regularly use pressurized air to perform “blowdowns” to remove dust from equipment surfaces and keep it from accumulating. However, blowdowns temporarily increase the amount of dust in the air, causing a respiratory hazard. This hazard can be reduced by using dust masks or other forms of respiratory protection.
For some related information on the hazards of airborne particles, please see our Respirator Basics online course and our Combustible Dust online course. We’ve included short sample videos of each below.
Respirator Basics Online Course
Combustible Dust Online Course
Noise
High noise levels are a serious hazard in most industrial environments. Prolonged exposure to the intense and high-pitched sounds of machinery can have damaging and lasting effects on the human ear.

Exposure to loud noise can result in:
- Temporary loss of hearing
- Permanent hearing loss from long-term exposure
- Ringing in the ears
- Damaged ear drums or bones from very loud blasts of noise
Workers should wear ear protection, like ear plugs and ear muffs, when working in known and designated loud areas.
For more information, check our hearing conservation online course (sample video below).
Chemicals
Papermaking facilities use a wide range of chemicals, including some that are quite hazardous.
You should have an understanding of the hazards associated with each chemical, and the necessary precautions to take when working with or near them.

It is important that all substances are properly labeled to ensure proper procedures are followed in the event of an incident. When working with chemicals, always refer to the Safety Data Sheet, formerly called the Material Safety Data Sheet. This document gives all of the known hazards and safety precautions for that substance.
To learn more about working with hazardous chemicals, including SDSs and more, you may want to check out our HazCom-GHS Online course (sample below).
Always wear all required personal protective equipment when working with chemicals. Know the location of all showers and eyewash stations in your work area. If you get chemicals in your eyes or on your skin, flush with water immediately to dilute the chemical and wash it away. Seek immediate medical attention. If you inhale chemical fumes and you are not certain of their hazard level, you should also seek immediate medical attention.
For more information about chemical hazards at a paper manufacturing facility, check out some of these online courses as well:
- Anhydrous Ammonia Awareness
- Chlorine Dioxide Awareness
- Formaldehyde Awareness
- Hydrogen Sulfide Awareness
- Turpentine Awareness
- Safety Showers and Eye Washes
- Process Safety Management (PSM)
Confined Spaces
A confined space, as defined by OSHA, is a space that:
- Is large enough that a person can work in it
- Has limited or restricted means for entry or exit
- Is not designed for continuous employee presence
Common examples of confined spaces in papermaking facilities include the interiors of pulp storage chests, dryer cans (including Yankee dryers), stock and water chests and tanks, and pulper vats.

Because confined spaces are mostly closed-off spaces, it is possible for hazardous gases to collect in them. Confined spaces can also lead to oxygen deficiency, which can lead to light-headedness and loss of consciousness.
Due to the high risks and dangers associated with confined spaces, all persons must be trained prior to participating in a confined space entry. An official checklist and procedure from the facility is required to show that the work in a confined space is safe and authorized. This form is called the Confined Space Work Permit.
For more information, check out our Confined Space Awareness online course and our Confined Space Entry-Permit Required online course.
Confined Space Awareness Online Course
Confined Space Entry-Permit Required Online Course
Water and Air Hoses
Water and air hoses are located throughout papermaking and paper converting facilities and pose unique hazards.
For example, hoses can get caught in machine nips. If a hose gets caught in an ingoing nip and it is wrapped around a person, that person could be pulled into the machine. To prevent this, always position the hose so that it is not behind you or going around any part of your body.
Another type of hazard comes from pressurized hoses. If a high pressure hose is turned on too quickly, the hose can be pulled from the worker’s grasp or cause the worker to lose his/her balance. To prevent this sudden jerking of the hose, open supply valves slowly.
If not controlled during use, a pressurized hose can whip around in the air or on the ground and hit workers. These whipping injuries can be very serious.

Hoses that are not properly stored can cause trip hazards, therefore, they should be coiled when not in use.
Fires
A fire can be a great safety issue anywhere. The most common fire hazards in a paper facility come from broke, litter, and dust being ignited. These materials are commonly found at the dry end of the paper machine and around the rewinders in the converting area.

Fires can be started by:
- Static electricity, which can cause sparks between the moving web and machine components
- Broke or dust build up on un-insulated steam or condensate lines
- Broke contacting heated surfaces on fork trucks and other mobile equipment
Airborne dust is a fire hazard and an explosion hazard, so it is important that dust is cleaned up and removed often. Even when dust control equipment is present, dust can accumulate on surfaces such as the upper surfaces of equipment, on building columns, and on roof trusses.
Keeping your paper machine and converting equipment clean and well-maintained is the most effective thing you can do to prevent fires.
See our Fire Safety and Fire Extinguisher Safety online courses for more information (we’ve provided short sample videos below).
Fire Extinguisher Safety Online Course
Paper Machine Hazard Controls: The Hierarchy of Controls, PPE, Lockout/Tagout, E-stops, and Housekeeping
Now let’s take a look at some general safety tips that can help in all situations.
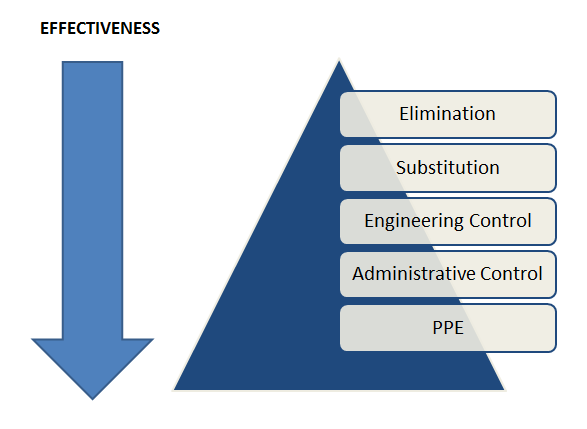
The Hierarchy of Controls
The single best thing to do when faced with hazards at work is to try to “control” them using the hierarchy of controls.
The basic idea of the hierarchy of controls is you should first try to eliminate a hazard, then try to create an engineering control, then a work practice control, and then use PPE, but only as a last resort. Plus, of course, you can use multiple controls for one hazard.
Please see our extended article on the Hierarchy of Controls for more information about this.
EHS Training Guide
Improve your EHS training now with tips from an ANSI/ASSP Z490 creator.
Yes! I Want this Guide!
Personal Protective Equipment
PPE is short for personal protective equipment. As you just learned, it’s the “last resort” in the hierarchy of controls.
PPE is just another name for equipment or clothing designed to keep you safe. All facilities have requirements for the necessary PPE when working in specific areas or doing specific jobs.
Examples of common PPE are:
- Hard hats
- Ear plugs
- Safety glasses
- Safety shoes
- Gloves

To work correctly, PPE must be comfortable and fit correctly. All PPE should be inspected for damages or defects before use. Do not use defective PPE and dispose of it properly.
Check out our online PPE training course for more information about this.
Lockout/Tagout
Lockout/tagout refers to a set of procedures designed to protect workers from the unexpected startup of machinery and equipment or the release of hazardous energy during service or maintenance activities. It involves shutting off electrical energy controls, draining lines, opening some valves and closing others, and other isolation activities. These settings should be verified, and locks or tags should then be used to ensure that these items do not re-energize or revert. Everyone performing work on a system must provide their own locks. This ensures that the system will not be re-energized until after all work is finished and all locks have been removed. If a system does not accommodate locks, a tag can be placed on the energy control stating that the device must not be operated.

Failing to properly lockout/tagout a piece of machinery can lead to many different injuries, including:
- Injuries resulting from working on or near a machine when it unexpectedly starts
- Cutting, crushing or other injuries caused by the unexpected movement of a machine component
- Electrocution caused by an electric current running through the machine
- Injuries resulting from the release of any type of stored energy, including hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, and thermal
For more on lockout, check out our online training courses for lockout/tagout for authorized employees and lockout/tagout for affected employees.
Lockout/Tagout for Authorized Employees Online Course
Lockout/Tagout for Affected Employees Online Course
E-Stops
Emergency stops, called E-stops for short, are large red buttons that, when pressed, bring a machine or system to an immediate stop to protect personnel and equipment. E- stops should be located within easy reach of all dangerous areas of a machine, especially the areas where workers perform their duties.

E-Stops should only be used in case of imminent or actual danger to personnel or equipment. In all other cases, the normal stop button or switch should be used.
Housekeeping
Housekeeping includes two basic activities: cleaning and organizing. A clean, organized facility will provide a more efficient and safer work environment for its employees. Poor housekeeping practices lead to messy, disorganized work areas, and also increase the number of workplace hazards.

You can help keep your facility clean and safe by following good housekeeping practices, such as:
- Keep all work area floors and walkways clear of trip hazards
- Return all tools and equipment to their proper storage locations when you are done using them
- Immediately clean up all spills
- Remove and properly process all paper broke and accumulated dust
For more information, check out our online courses on good housekeeping and 5S.
Summary: Paper Manufacturing Safety Tips
Like any industrial setting, a paper manufacturing facility presents a hazards to the people who work there. But by knowing how to identify hazards, to control them, and to implement general safe work practices (such as housekeeping), you’ll find work at a paper manufacturing facility can be safe, fun, and rewarding.
We hope you found these paper manufacturing safety tips helpful. Let us know your thoughts, especially if you’ve got some additional safety tips for paper manufacturing of your own to add.
To dig further into safety and safety training tips, you might enjoy:
- Manufacturing Safety Training Tips
- 10 Daily Workplace Safety Tips for Manufacturing
- How to Make Safety Training More Fun and Engaging
- 5 Manufacturing Safety Topics for a Safer Workplace
- What Is the Hierarchy of Controls?
- Safety Management Best Practices
- How to Conduct an Incident Investigation
- How to Conduct a Job Hazard Analysis in Four Steps
Let us know if you’d like more information about our online paper manufacturing courses and/or our online safety training courses. They’re available in many formats, including online streaming video, USB, video discs, and SCORM and AICC so you can import them into a learning management system (LMS).
And of course, if you’d like more information on paper manufacturing safety, you can do worse than click that link you just passed and see what OSHA has to say.